| єя«•«ьљƒ : ±Єњђ
|
ЅҐЉцєш»£ - 550221 263 |
| Comparison of Biomarkers for Predicting Prognosis in Heart Failure Patients with Dyspnea |
| к≥Дл™ЕлМАнХЩкµРл≥СмЫР |
| кєАнШХмД≠, л∞∞нХЬм§А, мЭінШЄл™Е, мЛ†нЩНмЫР, м°∞нШДмШ•, л∞ХнШХмД≠, мЬ§нШБм§А, м°∞мЬ§к≤љ, лВ®м∞љмЪ±, нЧИмКєнШЄ, кєАмЬ§лЕД, кєАкґМл∞∞ |
Background: Cystatin-C (Cys-C) has been considered as a useful marker of renal dysfunction that is associated with cardiovascular events. The aim of the present study was to evaluate Cys-C compared to renal biomarkers to predict adverse clinical outcomes.
Methods: From June 2008 to May 2010, the retrospective analyses included 717 consecutive heart failure (HF) patients presenting with dyspnea. At first enrollment, Cys-C and renal parameters including blood urea nitrogen (BUN), creatinine (Cr), and eGFR were obatained. The primary end point was the composite of cardiac death and rehospitalization for worsening HF.
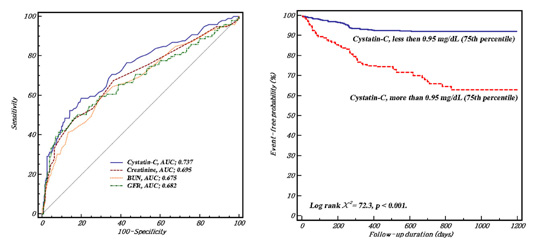
Results: During a median follow-up period of 731 days, 99 patients (13.8%) experienced clinical outcomes; 16 cardiac deaths and 83 HFs. Cys-C was significantly higher in patients with events (1.47 vs. 0.85 mg/dL, p<0.001). In addition, they showed higher BUN and Cr values, and lower eGFR. Among these parameters, Cys-C revealed the most favorable area under the curves, and patients with Cys-C<0.95mg/dL showed more frequent events (p<0.001). On multivariate Cox hazard analysis, Cys-C remained independently predictive of outcomes (HR 1.5, 95%CI 1.04-2.05).
Conclusion: In HF patients presenting dyspnea, Cys-C appears to be a more useful predictor of clinical events than other renal meausres.
|
|
|
Warning: getimagesize(/home/virtual/circulationadmin/renewal/econgress/conference/abstract/img_files/CysC1.jpg) [function.getimagesize]: failed to open stream: No such file or directory in /home/virtual/circulationadmin/new/econgress/conference/manage/schedule/view_abstract.php on line 164
|
|





