| єя«•«ьљƒ : ±Єњђ
|
ЅҐЉцєш»£ - 550197 175 |
| Pooled Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials Appraising the Efficacy and Safety of Cilostazol after Percutaneous Coronary Intervention |
| мЭЄм†ЬмЭШлМА лґАмВ∞л∞±л≥СмЫР¬є , мЭЄм†ЬмЭШлМА нХімЪілМА л∞±л≥СмЫР¬≤ , л©Фл¶ђлЖАл≥СмЫР¬≥ , лґАмВ∞мЭШлМАвБі |
| мЮ•мЮђмЛЭ¬є , м†ХмГБл†ђ¬є , мІДнХЬмШБ¬є , мДЬм†ХмИЩ¬є , мЦСнГЬнШД¬є , кєАлМАк≤љ¬є , л∞Хл≥ілѓЉ¬≤ , кєАлПЩкЄ∞¬≤ , кєАкЄ∞нЫИ¬≤ , мД§мГБнЫИ¬≤ , кєАлСРмЭЉ¬≤ , м°∞к≤љмЮД¬≥ , кєАл≥інШДвБі , л∞ХмЪ©нШДвБі , м†ЬнШХк≥§вБі , кєАлПЩмИШ¬є |
Background: Cilostazol has reduced restenosis and repeat revascularization in patients undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI). The objective of this study was to evaluate the impact of cilostazol on the angiographic and clinical outcomes in patients undergoing PCI with bare-metal stents (BMS) or drug-eluting stents (DES) and treated with aspirin and thienopyridine.
Methods: We searched MEDLINE, EMBASE, Cochrane databases, and conference proceedings for randomized controlled trials (RCTs) comparing triple antiplatelet therapy (aspirin, thienopyridine and cilostazol) with standard dual antiplatelet therapy. Pooled weighted mean difference (WMD) and pooled odds ratio (OR) with 95% confidence intervals (CIs) were calculated.
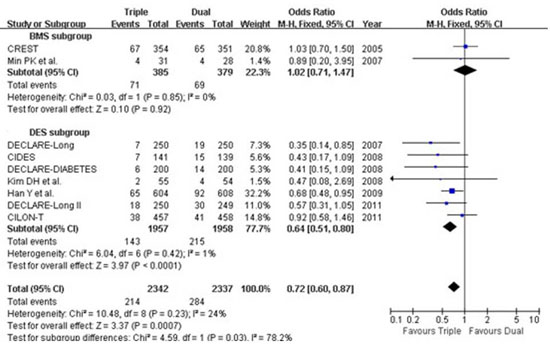
Results: A total of 10 RCTs including 4,770 patients with a median follow-up period of 6-12 months were included in the analysis. Pooled analysis showed that cilostazol was associated with a significant reduction in late loss (WMD 0.14, 95% CI 0.08–0.20, p<0.001) and angiographic restenosis (OR 0.58, 95% CI 0.48–0.71, p<0.001) for both DES and BMS and also individually. Triple antiplatelet therapy was associated with a significant reduction in target lesion revascularization (OR 0.55, 95% CI 0.40–0.76, p<0.001), with no difference in mortality (OR 0.79, 95% CI 0.49–1.28, p=0.34) or stent thrombosis (OR 1.01, 95% CI 0.43–2.38, p=0.99). Major adverse cardiac events were significantly lower in triple therapy group compared to dual therapy group (Figure). There was no significant difference in bleeding episodes between the two groups (OR 1.10, 95% CI 0.63–1.90, p=0.74).
Conclusions: Cilostazol in addition to dual antiplatelet therapy appears to be effective in reducing the risk of restenosis and repeat revascularization after PCI without any significant benefits for mortality or stent thrombosis.
|
|
|
Warning: getimagesize(/home/virtual/circulationadmin/renewal/econgress/conference/abstract/img_files/triplefigure.jpg) [function.getimagesize]: failed to open stream: No such file or directory in /home/virtual/circulationadmin/new/econgress/conference/manage/schedule/view_abstract.php on line 164
|
|





