| єя«•«ьљƒ : ±Єњђ
|
ЅҐЉцєш»£ - 550191 95 |
| Cytochrome P450 2C19 Polymorphism and Risk of Adverse Clinical Outcomes in Coronary Artery Disease Patients Treated with Clopidogrel: An Updated Meta-Analysis |
| мЭЄм†ЬмЭШлМА лґАмВ∞л∞±л≥СмЫР¬є , мЭЄм†ЬмЭШлМА нХімЪілМАл∞±л≥СмЫР¬≤ , л©Фл¶ђлЖАл≥СмЫР¬≥ , лґАмВ∞мЭШлМАвБі |
| мЮ•мЮђмЛЭ¬є , м†ХмГБл†ђ¬є , мІДнХЬмШБ¬є , мДЬм†ХмИЩ¬є , мЦСнГЬнШД¬є , кєАлМАк≤љ¬є , кєАлПЩкЄ∞¬≤ , мД§мГБнЫИ¬≤ , кєАлСРмЭЉ¬≤ , м°∞к≤љмЮД¬≥ , кєАл≥інШДвБі , л∞ХмЪ©нШДвБі , м†ЬнШХк≥§вБі , кєАлПЩмИШ¬є |
Background: CYP2C19 loss-of-function (LOF) polymorphisms have been postulated for lesser degrees of platelet inhibition and increased risk for recurrent ischemic events in coronary artery disease (CAD) patients on clopidogrel therapy. We performed a systematic review and meta-analysis of clinical trials to evaluate the risk of cardiovascular events in CAD patients on clopidogrel with and without CYP2C19 LOF polymorphism.
Methods: We searched MEDLINE, EMBASE, Cochrane databases, and conference proceedings. Genetic studies were included in which clopidogrel was initiated in predominantly invasively managed patients and in which clinical outcomes were ascertained. The primary end point was the occurrence of adverse clinical outcomes, as defined in each study by the occurrence of death, nonfatal myocardial infarction (MI), stent thrombosis or stroke.
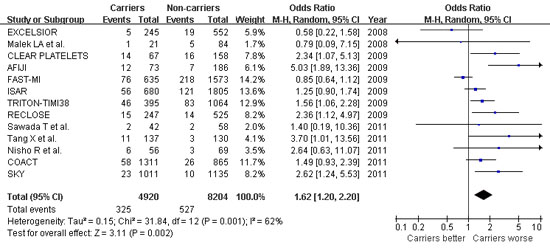
Results: A total of thirteen prospective cohort studies including 4,920 patients carrying CYP2C19 LOF allele and 8,204 patients with the wild-type genotype were included in this meta-analysis. Pooled analysis showed that CAD patients with CYP2C19 LOF allele were at significantly higher risk for adverse clinical events compared to CYP2C19 non-carriers during clopidogrel therapy (odds ratio [OR] 1.62, 95% confidence interval [CI] 1.20–2.20, p=0.002). The summary OR showed a significant association between the CYP2C19 LOF polymorphism and an increased risk of cardiac death (OR 2.18, 95% CI 1.37–3.47, p=0.001), MI (OR 1.42, 95% CI 1.12–1.81, p=0.004), and stent thrombosis (OR 3.10, 95% CI 2.08–4.61, p<0.001). Stratified analysis by the ethnicity of study population suggested higher odds of adverse clinical events in Eastern population (OR 1.89, 95% CI 1.32–2.72, p<0.001) compared with those in Western population (OR 1.46, 95% CI 1.00–2.14, p=0.05).
Conclusions: This meta-analysis indicates that CYP2C19 LOF polymorphism is associated with an increased risk of adverse clinical events in CAD patients on clopidogrel, especially in Asian population.
|
|
|
Warning: getimagesize(/home/virtual/circulationadmin/renewal/econgress/conference/abstract/img_files/2C19meta.jpg) [function.getimagesize]: failed to open stream: No such file or directory in /home/virtual/circulationadmin/new/econgress/conference/manage/schedule/view_abstract.php on line 164
|
|





