| єя«•«ьљƒ : ∆чљЇ≈Ќ
|
ЅҐЉцєш»£ - 540692 159 |
| Urinary albumin-creatinine ratio is related with augmentation index in patients with primary hypertension |
| к±ікµ≠лМАнХЩкµРмЭШл£МмЫР мЛђмЮ•нШИкіАлВік≥Љ ¬є, лґДлЛємДЬмЪЄлМАнХЩкµРл≥СмЫР мИЬнЩШкЄ∞лВік≥Љ¬≤ , мДЬмЪЄлМАнХЩкµРл≥СмЫР мИЬнЩШкЄ∞лВік≥Љ¬≥, к≥†л†§лМАнХЩкµР кµђл°Ьл≥СмЫР мЛђмЮ•лВік≥ЉвБі,к≥†л†§лМАнХЩкµР мХИмВ∞л≥СмЫР мЛђмЮ•лВік≥Љ5, м°∞мД†лМАнХЩкµРл≥СмЫР мИЬнЩШкЄ∞лВік≥Љ6, нХЬл¶ЉлМАнХЩкµР нХЬк∞ХмД±мЛђл≥СмЫР мИЬнЩШкЄ∞лВік≥Љ7, нХЬл¶ЉлМАнХЩкµР мД±мЛђл≥СмЫР мИЬнЩШкЄ∞лВік≥Љ 8 |
| нХЬмД±мЪ∞¬є, мЬ†кЈЬнШХ¬є ,мµЬлПЩм£Љ¬≤ ,мЭінХімШБ¬≥ ,кєАмЭСм£ЉвБі ,мЮДмГБмЧљ5 ,м†Хм§СнЩФ6 ,кєАлѓЉкЈЬ7 ,м°∞мГБнШЄ8 |
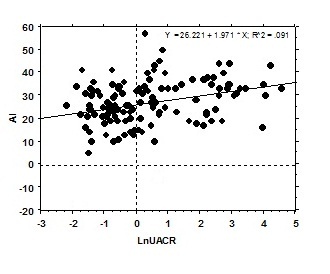
BACKGROUND: It has been demonstrated that microalbuminuria is a predictor of cardiovascular complications. But, the association between the degree of microalbuminuria and arterial dysfunction and morphological change is yet to be clarified. METHODS: In a group of 133 hypertensive patients (81 men, 49.910.1 yrs) from 5 university hospitals without gross proteinuria (Dipstick test<1+), diabetes, established cardiovascular complication. Urine albumin and creatinine concentration were measured with spot urine and expressed as mg/g. The augmentation index (AI) was obtained by applanation tonometry and carotid intima-media thickness (IMT) was measured with Manheim CIMT consensus protocol. Because of markedly skewd distribution, urinary albumin/creatinine ratio (UACR) was logarithmic transformed (lnUACR). Simple and multiple regression was performed to evaluate correlation between lnUACR and AI and IMT. RESULTS: lnUACR showed statistically significant positive correlation with AI (R2=0.096, p=0.0003). But there was no significant correlation with IMT. AI was positively correlated with age (R2=0.090, p=0.0105) and abdominal circumference (R2=0.070, p=0.0027). After multiple regression with age, abdominal circumference, systolic and diastolic blood pressure, lnUACR independently correlated with AI (p=0.0128). CONCLUSIONS: In hypertensive patients even without evidence of proteinuria, degree of microalbuminuria correlated with enhanced systolic augmentation of the arterial pressure, These findings suggest that worse cardiovascular outcomes with MA may be associated with the presence of an arterial dysfunction in hypertensive patients.
|
|
|
Warning: getimagesize(/home/virtual/circulationadmin/renewal/econgress/conference/abstract/img_files/UACRvsAIIMT.jpg) [function.getimagesize]: failed to open stream: No such file or directory in /home/virtual/circulationadmin/new/econgress/conference/manage/schedule/view_abstract.php on line 164
|
|





