| єя«•«ьљƒ : ∆чљЇ≈Ќ
|
ЅҐЉцєш»£ - 540599 164 |
| Comparison of Long-Term Clinical Outcomes of First Generation Sirolimus-/Paclitaxel-Eluting Stents and Second Generation Zotarolimus-/Everolimus-Eluting Stents in Patients With ST-Elevation Myocardial Infarction |
| мЭЄм†ЬмЭШлМА лґАмВ∞л∞±л≥СмЫР¬є, мЭЄм†ЬмЭШлМА нХімЪілМАл∞±л≥СмЫР¬≤ , мШБлВ®мЭШлМА¬≥ , к≥Дл™ЕмЭШлМАвБі |
| мЮ•мЮђмЛЭ¬є, м°∞мШБмЩД¬є, мІДнХЬмШБ¬є, мЦСнГЬнШД¬є, кєАлМАк≤љ¬є, кєАлПЩмИШ¬є, кєАлСРмЭЉ¬≤ , кєАлПЩкЄ∞¬≤ , кєАмШБм°∞¬≥ , л∞ХмҐЕмД†¬≥ , мЬ§нШБм§АвБі, кєАмЬ§лЕДвБі |
Background: Sirolimus-eluting stents (SES) and paclitaxel-eluting stents (PES) seem to be superior to bare metal stents in terms of clinical outcome in patients with ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI), but there are few comparisons of outcomes of zotarolimus-eluting stents (ZES) and everolimus-eluting stents (EES). We assessed the hypothesis that second-generation drug-eluting stents (DES) are not inferior to first-generation DES in primary intervention for STEMI.
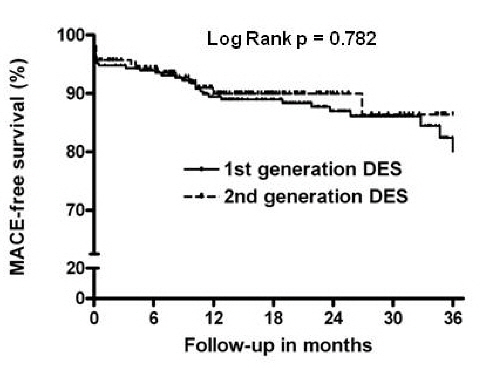
Methods: Of total 431 patients with STEMI, 260 patients were treated with first-generation DES and 171 patients were treated with second-generation DES. Mean follow-up duration was 18 months. The primary end point was 3-year composite rate of major adverse cardiac events (defined as death, MI, or ischemia-driven target vessel revascularization). Secondary end points included the individual components of the primary end point, late loss, angiographic restenosis, and stent thrombosis.
Results: Baseline clinical characteristics were similar between the two groups. At 8-month angiographic follow-up, the late loss was significantly lower in EES and SES compared with ZES and PES (0.08 ± 0.41 vs. 0.23 ± 0.50 mm vs. 0.50 ± 0.64 vs. 0.61 ± 0.69 mm, respectively, p < 0.001). Moreover, EES showed a significantly lower restenosis rate compared with the other stents (SES 11.5% vs. PES 16.7% vs. ZES, 21.6% vs. EES, 2.3%, p = 0.050). At 3-year follow up, cumulative incidence rates of primary end points in the first- and second-generation DESs were 14.2% and 11.1% (p = 0.346). Stent thrombosis occurred in 3 patients in the SES group and 2 patients in the ZES group (p = 0.254).
Conclusions: Despite the differences in restenosis rate and late loss in the 4 different DES, Second-generation DES, as compared with first-generation DES, showed similar, acceptable results in the treatment of STEMI.
Keywords: Myocardial infarction, Drug-eluting stents
|
|
|
Warning: getimagesize(/home/virtual/circulationadmin/renewal/econgress/conference/abstract/img_files/Injefigure.jpg) [function.getimagesize]: failed to open stream: No such file or directory in /home/virtual/circulationadmin/new/econgress/conference/manage/schedule/view_abstract.php on line 164
|
|





