| єя«•«ьљƒ : ∆чљЇ≈Ќ
|
ЅҐЉцєш»£ - 530431 215 |
| Comparison Unfractionated Heparin and Low Molecular Weight Heparin on Long-term Clinical Outcome in Patients with ST-Elevation Myocardial Infarction |
| к≤љнЭђлМАнХЩкµРл≥СмЫР мИЬнЩШкЄ∞лВік≥Љ, лМАнХЬмЛђмЮ•нХЩнЪМ Korean Acute Myocardiac Infarction Registry (KAMIR) |
| мЪ∞мҐЕмЛ†, кєАмЫР, мЬ†нГЬк≤љ, кґМмД±мІД,нХШмГБмІД, кєАмДЭмЧ∞, кєАмИШм§С, кєАмЪ∞мЛЭ, кєАл™Ек≥§, кєАкґМмВЉ, л∞∞мҐЕнЩФ, Korean Acute Myocardiac Infarction Registry (KAMIR)мЧ∞кµђмЮР |
Background: The inhibition of thrombin plays a key role as adjunct therapy in the management of patients with primary percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) for ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI). The objective of this study is to compare the effectiveness of unfractionated heparin (UFH) and low molecular weight heparin (LMWH) in patients with STEMI in Korea.
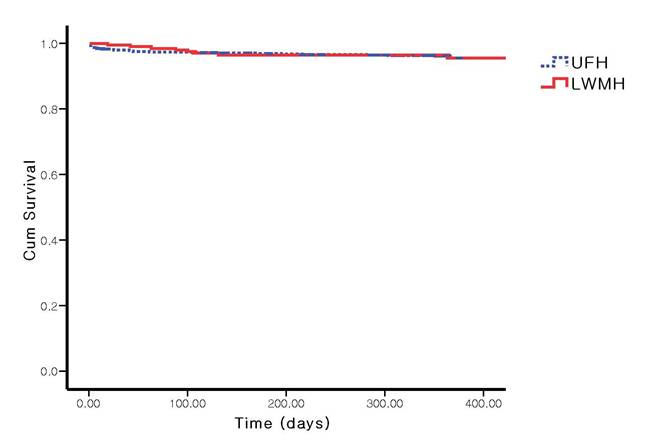
Methods: We analyzed data of 791 patients with STEMI and either antiplatelet therapy with UFH or with LMWH, which were prospectively enrolled in the KAMIR. Intravenous UFH (n = 597) or LMWH (n = 194) was to be administered. Complications, in-hospital mortality, 1-month, 6-month, and 12-month major adverse cardiac events (MACE) were evaluated.
Results: There were no defferent between the two groups in the angiographic characteristics such as B2/C lesion, multi-vessel coronary lesion, pre-TIMI 0/1 grade flow. During the 1-month follow-up, all-cause death or nonfatal myocardial infarction occurred in 2.3% (14/597) of patients treated by UFH and 2.1% (4/194) of patients treated by LMWH (p=0.72). There was no significant difference in the incidences of complications [127/597 (21.3%) vs 32/194 (16.5%)], in-hospital mortality [6/597 1.0%) vs 0/194 (0.0%)]. Bleeding complications was occurred in 0.5% (3/597) of patients treated by UFH and 1.0% (2/194) of patients treated by LMWH (p=0.42). There was no significant difference in the incidences of all-cause-death, stent thrombosis, and target vessel revascularization during 6-month and 12-month follow-up.
Conclusions: LMWH was not inferior to UFH for the treatment of patients with STEMI in Korea. LMWH is a safe and effective alternative to UFH with advantages of convenience.
|
|
|
Warning: getimagesize(/home/virtual/circulationadmin/renewal/econgress/conference/abstract/img_files/figureLMWH.jpg) [function.getimagesize]: failed to open stream: No such file or directory in /home/virtual/circulationadmin/new/econgress/conference/manage/schedule/view_abstract.php on line 164
|
|





