- 고혈압의 병태생리면역, 염증 반응은 고혈압을 유발하는 주요한 병인 기전이다
- 고혈압의 병태생리노인성 심혈관 질환의 주범 중 하나인 혈관 노화는 DNA 손상에 의해 유발될 수 있다.
- 고혈압의 병태생리고혈압은 좌심실 수축기능이 보전된 심부전 발생의 가장 큰 기여인자다
- 고혈압의 병태생리 이차성 고혈압의 원인인 섬유근육형성이상의 유병률은 증가하고 있다
- 고혈압의 진단자가 혈압모니터 어디까지 왔고 어디로 가나
- 고혈압의 진단야간고혈압, 손목혈압계 다시 주목받나
- 고혈압의 진단효과적인 고혈압 진단 및 치료를 위한 새로운 전략
- 고혈압의 치료3제 고정용량복합제는 고혈압 치료의 새로운 장을 열 것이다
- 고혈압의 치료코로나 19시기 혈압 조절의 정도는 심혈관질환의 발생에 어떤 영향을 미칠까
- 고혈압의 치료임신성 고혈압의 응급 상황에서는 라베탈롤, 하이드랄라진, 속효성 경구 니페디핀을 사용한다
- 고혈압의 치료고위험 고혈압 환자에서 신장신경차단술은 효과적이다
고위험 고혈압 환자에서 신장신경차단술은 효과적이다
Renal Denervation: A Novel Approach to Hypertension Care
2021 ESH-ISH Meeting에서 renal denervation 관련 A Novel Approach to Hypertension Care라는 제목으로 고위험군 환자에서 renal denervation의 임상적 효과에 대해 발표된 내용이 있어 소개하도록 하겠다.
Renal denervation이 다양한 위험인자를 가진 고혈압 환자에서 효과적인지 알아보기 위해 GSR (Global proSpective registrY for syMPathetic renaL denervatIon in seleCted IndicatIons Through 3 Years Registry)에 등록된 2,652명의 고위험 환자를 대상으로 3년간 혈압 강압효과와 부작용 유무를 조사하였다. 고위험군은 resistant HTN, 65세이상, DM, isolated systolic HTN, chronic kidney disease, afib으로 정하였다. 3년째 24시간 SBP 감소는 전체환자에서는 −8.9±20.1 mm Hg, resistant HTN에서는 −10.4±21.0 mm Hg, 65세이상에서는 −8.7±17.4 mm Hg, DM 환자에서는 −10.2±17.9 mm Hg, isolated systolic hypertension에서는 −8.6±18.7 mm Hg, chronic kidney disease에서는 −10.1±20.3 mm Hg였고(그림1), 모든 그룹에서 baseline에 비해 통계적으로 의미 있게 감소하였다(p < 0.0001). Atherosclerosis cardiovascular disease (ASCVD) risk score에 따른 6개월, 1년, 2년, 3년째 강압효과 역시 비슷한 결과를 보였고, 3년 adverse event는 baseline ASCVD risk에 비례해서 증가함을 보여주었다.
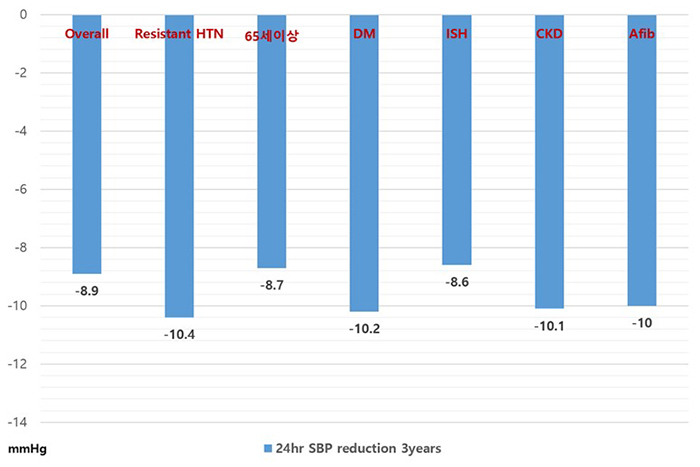 그림 1. 여러 위험군에서 3년째 24시간 SBP 감소 효과
그림 1. 여러 위험군에서 3년째 24시간 SBP 감소 효과
Safety and efficacy of RDN for resistant HTN with CKD
이 연구는 이탈리아 uncontrolled HTN 40명을 대상으로 renal denervation의 3개월, 6개월, 1년째 efficacy와 safety를 조사한 연구로 21명의 환자는(52,5%) eGFR<45ml/min 이하인 chronic kidney disease 환자였다. 치료 반응 군은 ambulatory SBP의 5mmHg이상의 감소, office SBP는 10mmHg 이상의 감소가 있는 경우로 정의하였다. 치료 반응 군은 74.4%(29명)에 달하였고, 전체 환자에서 1년째 office SBP는 −19.7±27.1 mmHg, ambulatory SBP는 −13.9±23.6 mmHg감소 하였고, eGFR이 낮은 환자에서는 1년째 office SBP는 −19.4±31.6 mmHg, ambulatory SBP는 −18.0±23.4 mmHg감소 하였고, GFR이 높은 환자(office SBP는 −19.9±23.6 mmHg, ambulatory SBP는 −9.8±24.6 mmHg 감소)와 차이가 없었다 (그림2). 또한 주요 부작용은 관찰되지 않았다. 하지만, 단일센터 연구이고 환자수가 적은 것을 고려하여 해석에 주의를 요할 것으로 판단된다.
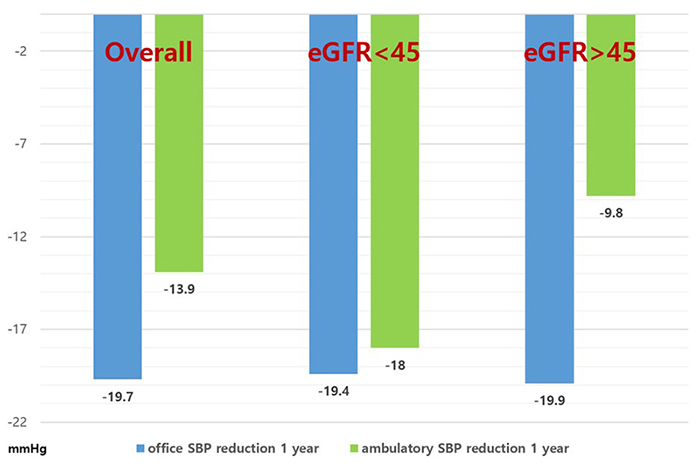 그림 2. 1 year office SBP & ambulatory SBP 감소
그림 2. 1 year office SBP & ambulatory SBP 감소
SYMPLICITY 3 trial에서 renal denervation의 효과를 충분히 입증하지 못하여, renal denervation의 관심도가 많이 감소하긴 하였으나, 여전히 renal denervation이 도움을 줄 수 있는 환자 그룹을 찾기 위한 추가적인 연구들이 진행 중이다. 현재 renal denervation 연구에서 관건은 반응이 좋을 것으로 예측되는 환자 군을 찾는 것과 강압효과가 장기간 유지될 것인가 라는 문제인데, 위 두 연구에서 CKD를 포함한 여러 고위험군에서의 효과를 입증하였고, 또한 GSR연구에서는 3년 long term durability도 입증하여 향후 renal denervation 연구에 숨통을 터주는 첫걸음이 될 것으로 판단된다. 추후 이 두 연구에 언급된 고위험군들 에서의 randomized controlled trial 들이 진행되어 좋은 결과가 나오길 기대해본다.
참고문헌
1) Felix Mahfoud , Giuseppe Mancia , Roland Schmieder , Krzysztof Narkiewicz , Luis Ruilope , Markus Schlaich , Robert Whitbourn , Andreas Zirlik , Thomas Zeller, Philipp Stawowy, Sidney A Cohen, Martin Fahy, Michael Böhm. Renal Denervation in High-Risk Patients With Hypertension. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2020; 75:2879-2888.
2) Stephen C Textor. Renal Denervation and International Registry Data: Where Are We Now? J Am Coll Cardiol. 2020; 75:2889-2891.
3) Federico Marin, Simone Fezzi, Alessia Gambaro, Francesco Ederle, Gianluca Castaldi, Maddalena Widmann, Concetta Gangemi, Valeria Ferrero, Gabriele Pesarini, Michele Pighi, Flavio L Ribichini. Insights on safety and efficacy of renal artery denervation for uncontrolled-resistant hypertension in a high risk population with chronic kidney disease: first Italian real-world experience. J Nephrol . 2021 Jan 22. Online ahead of print.



