| єя«•«ьљƒ : ±Єњђ
|
ЅҐЉцєш»£ - 550412 7 |
| Impact of Preexisting Cerebral Ischemia Detected by Magnetic Resonance Imaging and Angiography on Clinical Outcomes After Coronary Artery Bypass Graft in Patients Without History of Stroke |
| мЪЄмВ∞лМАнХЩкµР мЭШк≥ЉлМАнХЩ мДЬмЪЄмХДмВ∞л≥СмЫР |
| кєАмЫРмЮ•, мЮ•мД†м£Љ, л∞ХмЪ©кЈЬ, л∞Хк≤љлѓЉ, кєАмЪ©кЈ†, мХИм†ХлѓЉ, мЭімҐЕмШБ, л∞ХлНХмЪ∞, к∞ХмИШмІД, мЭімКєнЩШ, кєАмШБнХЩ, мЭім≤†нЩШ, л∞ХмД±мЪ±, л∞ХмКєм†Х |
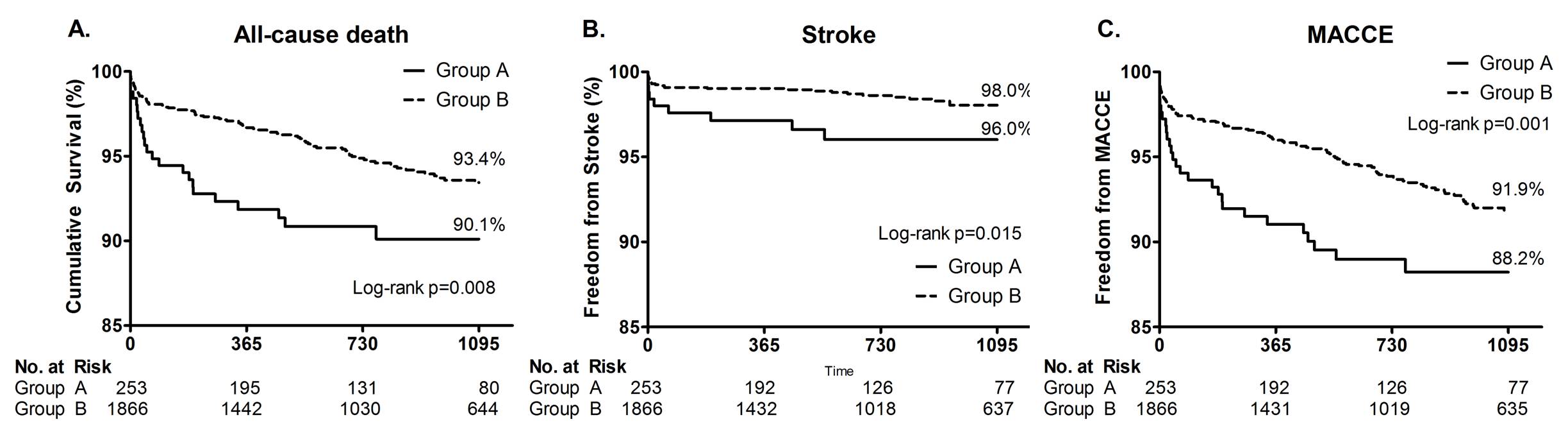
Background: Limited data existed for long-term clinical outcomes of asymptomatic brain ischemia after coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG). We sought to assess the impact of preexisting ischemia detected by brain magnetic resonance imaging and angiography (MRA) on clinical outcomes after CABG. Methods: Between Jan. 2003 and May 2009, 3,071 patients underwent CABG in Asan Medical Center. Preoperative brain MRA was performed in 2,417 patients. Patients with history of stroke were excluded and total 2,119 patients were analyzed. Ischemia was detected by brain MRA in 253 patients (group A), but not in 1866 patients (group B). Preoperative characteristics, follow-up survival, and cardiac and neurological events were investigated.Results: The median follow-up period was 2.2 years. Univariate analysis showed that patients in group A (65.4 ± 8.3 years) were older than those in group B (63.0 ± 9.0 years) (p<0.001). Diabetes mellitus was more common in group A (48.6%) than group B (40.9%) (p=0.019). The prevalence of chronic kidney disease was higher in group A (63 patients: 24.9%) compared with group B (324 patients: 17.4%) (p=0.004). The prevalence of peripheral vascular disease was higher in group A (13 patients: 5.1%) than in group B (39 patients: 2.1%) (p = 0.003). Euroscore was higher in group A (4.3 ±2.3) than group B (3.6 ±2.2) (p<0.001). Survival rate was significantly lower (93.4% vs. 90.1%, p = 0.008), and freedom from stroke or major adverse cardiac and cerebrovascular event were significantly lower in group A (98.0% vs. 96.0%, p = 0.015, and 91.9% vs. 88.2%, p = 0.001). Conclusions: Preexisting ischemic findings on brain MRA in patients who undergoing CABG were related to death, stroke, and major adverse cardiac and cerebrovascular event.
|
|
|
Warning: getimagesize(/home/virtual/circulationadmin/renewal/econgress/conference/abstract/img_files/ischemiaFig1.jpg) [function.getimagesize]: failed to open stream: No such file or directory in /home/virtual/circulationadmin/new/econgress/conference/manage/schedule/view_abstract.php on line 164
|
|





