| єя«•«ьљƒ : ±Єњђ
|
ЅҐЉцєш»£ - 530960 311 |
| A Point-of-Care Assay Could Identify High Platelet Reactivity After Clopidogrel Therapy and Impact of Triple Anti-Platelet Therapy on Platelet Reactivity in Type 2 Diabetic Patients |
| мЭЄм†ЬлМАнХЩкµР лґАмВ∞л∞±л≥СмЫР¬є , мШБлВ®лМАнХЩкµР л≥СмЫР¬≤ , к≥Дл™ЕлМАнХЩкµР лПЩмВ∞л≥СмЫР¬≥ |
| кєАлПЩкЄ∞¬є, мЦСнГЬнШД¬є , кєАлСРмЭЉ¬є ,кєАлПЩмИШ¬є ,мЭімГБнЭђ¬≤ ,нЩНкЈЄл£®¬≤ ,л∞ХмҐЕмД†¬≤ , кєАмШБм°∞¬≤ , л∞ХнШХмД≠¬≥ ,м°∞мЬ§к≤љ¬≥ ,нЧИмКєнШЄ¬≥ ,кєАкґМл∞∞¬≥ |
Background: High platelet reactivity and impaired response to clopidogrel are common in type 2 diabetic patients. P2Y12 reaction unit (PRU) вЙ•240 after clopidogrel therapy, measured by a point-of-care assay, is associated with higher risk of adverse event after coronary stent implantation.
Methods: We used a point-of-care assay (VerifyNow system) to evaluate the impact of diabetes mellitus on residual platelet reactivity in 544 patients undergoing dual or triple anti-platelet therapy who underwent DES implantation. All patients received a single 300 to 600 mg clopidogrel loading dose followed by 75 mg of clopidogrel daily and 100 mg of aspirin daily. Cilostazol daily dose of 200 mg was added in some patients by the discretion of the operators.
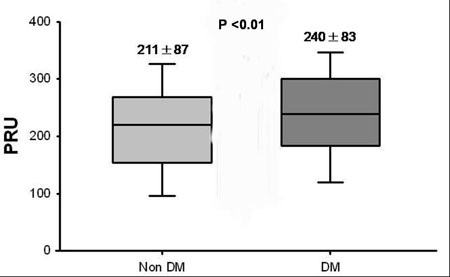
Results: Platelet reactivity assessed by a point-of-care assay was higher in type 2 diabetic patients. Diabetic patients, compared with non-diabetic patients, manifested: 1) higher PRU value (Figure); 2) higher incidence of high platelet reactivity (HPR) which was defined as PRU вЙ•240 after clopidogrel therapy. We also found that higher PRU value and higher incidence of HPR noted in diabetic patients were consistent in patients undergoing triple anti-platelet therapy as well as dual anti-platelet therapy, however, higher PRU value and higher incidence of HPR in diabetic patients decreased with triple anti-platelet therapy.
Conclusion: Type 2 diabetes mellitus is associated with high platelet reactivity and impaired response to clopidogrel, as assessed by a point-of-care assay. Addition of cilostazol to double anti-platelet therapy decrease PRU value and the incidence HPR in type 2 diabetic patients.
|
|
|
Warning: getimagesize(/home/virtual/circulationadmin/renewal/econgress/conference/abstract/img_files/VerifyNow.jpg) [function.getimagesize]: failed to open stream: No such file or directory in /home/virtual/circulationadmin/new/econgress/conference/manage/schedule/view_abstract.php on line 164
|
|





