| єя«•«ьљƒ : ∆чљЇ≈Ќ
|
ЅҐЉцєш»£ - 530947 34 |
| What Kind of Risk Factors Can Predict in Acute Coronary Syndrome? |
| лМАкµђ к∞АнЖ®л¶≠лМАнХЩ л≥СмЫР мИЬнЩШкЄ∞ лВік≥Љ |
| м†ХмІДмЪ±, кєАкЄ∞мЛЭ, кєАл≥СнШЄ, кєАл≥СкЈЬ, нХШкЈЉмІД, л∞∞к≤љл•Ь, мД±л™Ем§А, кєАм†ХнШД, кєАмЖМмЧ∞, мЭімШБмИШ, мЭімІДл∞∞, л•ШмЮђкЈЉ, мµЬмІАмЪ©, мЮ•мД±кµ≠ |
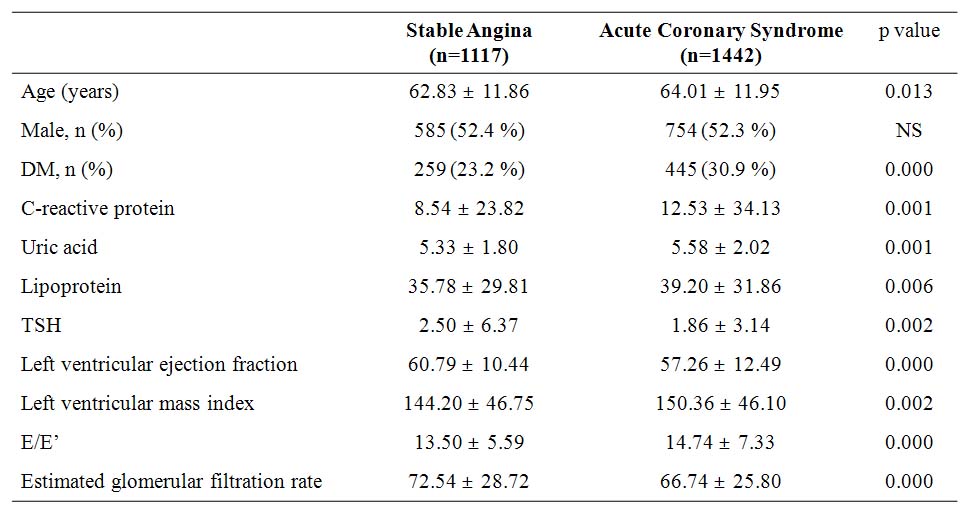
Background: As hypertension and diabetes mellitus increase, the number of patients developing acute coronary syndrome (ACS) associated with conventional risk factors is increasing. The differentiation between stable angina and ACS is prognostically important, because the management is different. This study aimed to analyze the independent predictor of ACS in patients with ischemic heart disease (IHD). Methods: We conducted a retrospective analysis of collected data on 2559 consecutive patients who had been hospitalized with IHD between May 2006 and April 2009 at our centers. We assessed demographic (age, sex) and clinical characteristics and echocardiographic and laboratory findings. The estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) was calculated by the Modification of Diet in Renal Disease Study Group (MDRD) formula. Results: The patients were divided into stable angina (AP) group (1117 patients, mean age 63 yr, male 585) and ACS group (1442 patients, mean age 64 yrs, male 754). There was higher incidence of diabetes and older age in ACS. The patients in ACS had lower left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) and higher left ventricular mass indes and E/EвАЩ ratio. The level of C-reactive protein, uric acid and lipoprotein in ACS were significantly higher compared to those in AP. The level of TSH and eGFR in ACS were significantly lower compared to those in AP. After adjustment for several significant parameters, using a Cox proportional hazards model, reduced eGFR (adjusted p = 0.000; odds ratio [OR] 0.993), DM (adjusted p = 0.000; OR 1.409), TSH (adjusted p = 0.002; OR 0.938), and reduced LVEF (adjusted p = 0.000; OR 0.982) were identified as significant independent predictors for ACS in patients with IHD. Conclusions: This study was showed that a reduced eGFR, DM, hyperthyroidism, and reduced LVEF are independent predictors for ACS in patients with IHD. Estimation of the eGFR, DM, hyperthyroidism, and LVEF might be used as prognostic value in these patients.
|
|
|
Warning: getimagesize(/home/virtual/circulationadmin/renewal/econgress/conference/abstract/img_files/PredictorinACS.jpg) [function.getimagesize]: failed to open stream: No such file or directory in /home/virtual/circulationadmin/new/econgress/conference/manage/schedule/view_abstract.php on line 164
|
|





