| єя«•«ьљƒ : ±Єњђ
|
ЅҐЉцєш»£ - 530931 270 |
| Relationship between central blood pressure and target organ damage in first diagnosed hypertension patients |
| лМАкµђк∞АнЖ®л¶≠лМАнХЩл≥СмЫР мИЬнЩШкЄ∞лВік≥Љ |
| мД±л™Ем§А, кєАкЄ∞мЛЭ, л∞∞к≤љл•Ь, нХШкЈЉмІД, кєАл≥СкЈЬ, кєАл≥СнШЄ, кєАнЪ®мІД, кєАм†ХнШД, м†ХмІДмЪ±, кєАмЖМмЧ∞, мЭімШБмИШ, мЭімІДл∞∞, л•ШмЮђкЈЉ, мµЬмІАмЪ©, мЮ•мД±кµ≠ |
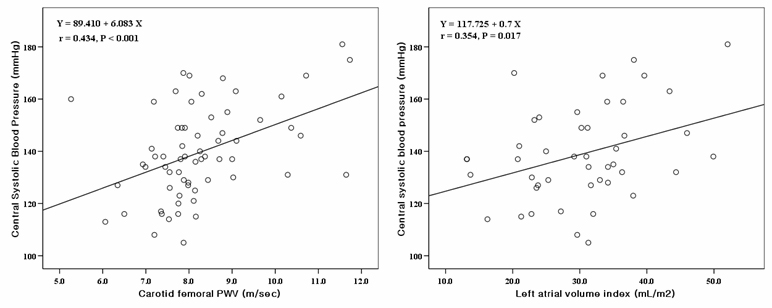
Purpose: Central pressures are pathophysiologically more relevant than peripheral pressures for the pathogenesis of cardiovascular disease. In CAFE study, central pressure independently predicts outcome in treated patients with hypertension. The aim of this study was to evaluate relationship central blood pressure (BP) and target organ damage in first diagnosed hypertension patients. Methods: We enrolled 163 patients (mean age 48.4±13.1 yrs, male 88 (54.0 %)), who was recently diagnosed as hypertension. Hypertension was diagnosed as day time systolic/diastolic BP > 135/85mmHg by ambulatory BP monitoring. We compared central BP, estimated glomerular filtration rate (GFR), carotid-femoral PWV(cfPWV), left ventricular mass index and left atrial volume index (LAVI). Results: The mean 24hr average systolic BP for day time and central systolic BP were 145.1±14.0 and 139.6±17.7 mmHg, respectively. Central systolic BP was significantly correlated to age (r=0.295, p=0.018), estimated GFR (r=-0.304, p=0.025), cfPWV (r=0.434, p<0.0001) and LAVI (r=0.354, p=0.017). In multivariate regression analysis, the central BP was independently correlated to estimated GFR and LAVI after adjustment of age and PWV. Conclusions: Central BP might be associated to target organ damage in hypertension patients. However, further larger study might be needed.
|
|
|
Warning: getimagesize(/home/virtual/circulationadmin/renewal/econgress/conference/abstract/img_files/CentralBPandABP.jpg) [function.getimagesize]: failed to open stream: No such file or directory in /home/virtual/circulationadmin/new/econgress/conference/manage/schedule/view_abstract.php on line 164
|
|





