| єя«•«ьљƒ : ±Єњђ
|
ЅҐЉцєш»£ - 530918 56 |
| The pro-BNP could predict Re-hospitalization in Congestive Heart Failure |
| лМАкµђ к∞АнЖ®л¶≠лМАнХЩ л≥СмЫР мИЬнЩШкЄ∞ лВік≥Љ |
| м†ХмІДмЪ±, кєАкЄ∞мЛЭ, кєАл≥СнШЄ, кєАл≥СкЈЬ, нХШкЈЉмІД, л∞∞к≤љл•Ь, мД±л™Ем§А, кєАм†ХнШД, кєАмЖМмЧ∞, мЭімШБмИШ, мЭімІДл∞∞, л•ШмЮђкЈЉ, мµЬмІАмЪ©, мЮ•мД±кµ≠ |
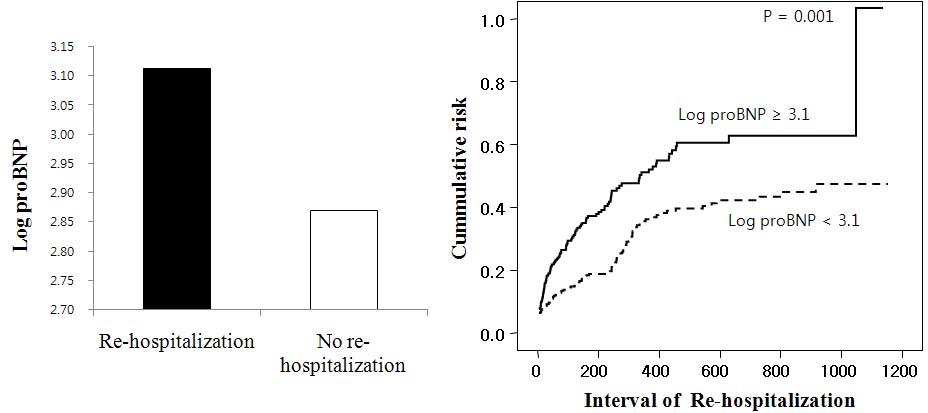
Background: Patients with chronic congestive heart failure (CHF) require frequent re-hospitalization because of the exacerbation of CHF. It is of clinical importance to determine predicting factors for re-hospitalization to reduce this likelihood. The aim of our study is to evaluate predicting factors for re-hospitalization among patients who had been hospitalized with CHF. Methods: We conducted a retrospective analysis of collected data on 737 consecutive patients who had been hospitalized with CHF between May 2006 and April 2009 at our centers. We assessed demographic and clinical characteristics and echocardiographic and laboratory findings. Results: The patients were divided into re-hospitalized group (RH) (205 patients, mean age 69 yr, male 102, mean follow duration 176 days) and no re-hospitalized group (NRH) (532 patients, mean age 70 yrs, male 277, mean follow duration 427 days). There was higher incidence of diabetes in RH. The patients in RH had lower ejection fraction and higher E/A ratio. The level of C-reactive protein, log pro-BNP, uric acid and apo-lipoprotein b/a in RH were significantly higher compared to those in NRH. After adjustment for several significant parameters, using a Cox proportional hazards model, log pro-BNP (adjusted p=0.001; odds ratio 1.421) and E/A ratio (adjusted p=0.042; odds ratio 1.251) were independent predictors of re-hospitalization. Conclusions: The level of pro-BNP and E/A ratio might be independent predictors of re-hospitalization among patients who had been hospitalized with CHF. Therefore interventions to decrease re-hospitalization should do also target management in all hospitalized patients.
|
|
|
Warning: getimagesize(/home/virtual/circulationadmin/renewal/econgress/conference/abstract/img_files/RehospitalizationinCHF.jpg) [function.getimagesize]: failed to open stream: No such file or directory in /home/virtual/circulationadmin/new/econgress/conference/manage/schedule/view_abstract.php on line 164
|
|





