| єя«•«ьљƒ : ±Єњђ
|
ЅҐЉцєш»£ - 530644 314 |
| Pre-procedural Platelet Inhibition after 300-mg Loading Dose of Clopidogrel in Asian Patients undergoing scheduled Percutaneous Coronary Intervention |
| к≤љмГБлМАл≥СмЫР мИЬнЩШкЄ∞лВік≥Љ |
| к∞ХлѓЉк≤љ, м†ХмШБнЫИ, мЬ§мД±мЭА, к≥†мІДмЛ†, кєАмЭЄмИЩ, л∞ХмЪ©нЪМ, нЩ©мДЭмЮђ, к≥љмґ©нЩШ, нЩ©мІДмЪ© |
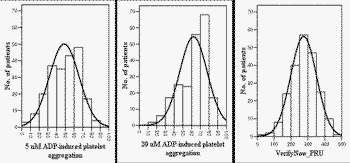
BACKGROUND: Platelet inhibitory response to clopidogrel varies considerably among individuals and pre-procedural platelet inhibition influences clinical outcomes after percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI). Because the CYP 2C19 mutant allele (*2 or *3) is more frequently identified in East Asian population than in Caucasian cohorts, pre-procedural platelet reactivity (PR) in East Asian patients may be greater compared with those of Caucasian. METHODS: We assessed the level of PR at least 12 h after 300-mg loading-dose (LD) of clopidogrel in patients undergoing scheduled PCI (n = 215). PR was measured with conventional aggregometry and VerifyNow. High post-clopidogrel platelet reactivity (HPPR) was defined as 5 ќЉmol/l ADP-induced PRmax вЙ• 50%. RESULTS: With 5 and 20 ќЉmol/l ADP stimuli, maximal PR (PRmax) were 48.7 ¬± 17.2% and 62.1 ¬± 15.7%, respectively, and the rate of HPPR reached to 51.9%. P2Y12 reaction unit (PRU) value was 274 ¬± 76 and 70% of patients showed PRU вЙ• 240. In patients who performed CYP 2C19 genotyping (n = 176), PRmax was significantly higher in the carrier of at least one CYP 2C19 mutant allele (50.8 ¬± 16.5 vs. 44.7 ¬±17.4, P = 0.008). In multivariate regression analysis, CYP 2C19 polymorphism was an independent predictor of HPPR (odds ratio 2.60, 95% confidence interval 1.36 to 4.95, P =0.004). The impact of CYP2C19*2 and *3 carriage on reduced response to clopidogrel did not differ. CONCLUSIONS: Pre-procedural PR after 300-mg LD of clopidogrel is higher in Asian patients undergoing scheduled PCI than in Caucasian. It may implicate a higher risk of ischemic events after PCI in Asian patients, which is mainly related with higher rate of the CYP2C19 mutant allele carriage in this population.
|
|
|
Warning: getimagesize(/home/virtual/circulationadmin/renewal/econgress/conference/abstract/img_files/circulation_figure_2.gif) [function.getimagesize]: failed to open stream: No such file or directory in /home/virtual/circulationadmin/new/econgress/conference/manage/schedule/view_abstract.php on line 164
|
|





