| єя«•«ьљƒ : ±Єњђ
|
ЅҐЉцєш»£ - 530130 171 |
| Ruptured thin-capped fibroatheromas in acute ST elevation myocardial
infarction: A virtual histology intravascular ultrasound analysis
|
| м§СмХЩлМАнХЩкµРл≥СмЫР мИЬнЩШкЄ∞лВік≥Љ мЛђмЮ•нШИкіАмДЉнД∞¬є , Cardiovascular Research Foundation¬≤ , Washington Hospital Center¬≥ |
| кєАмГБмЪ±, Gary S. mintz¬≤, мЭімЩХмИШ, мДЬмЮђмКє, мЭікіСм†Ь, мµЬм£ЉмЫР, нЩНм§АнЩФ, кєАнГЬнШЄ, кєАмєШм†Х, м°∞лМАмЬ§, Neil Weissmann¬≥,л•ШмЩХмД± |
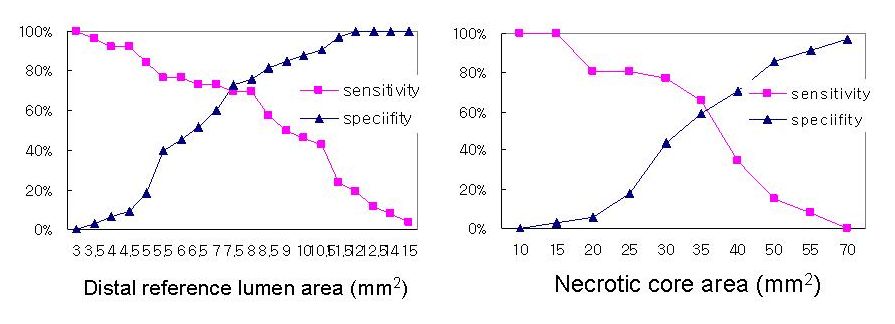
We assessed Virtual Histology Intravascular Ultrasound (VH-IVUS) thin-capped fibroatheromas (VH-TCFAs) in pts with acute ST elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI). VH-TCFAs were defined as necrotic core (NC) >10% of plaque area, plaque burden >40%, and NC in contact with the lumen for вЙ•3 image slices. Remodeling index (RI) was lesion/reference external elastic membrane >1.05. Results. Between Feb 2007 and April 2009, 110 pts presented with STEMI. VH-IVUS imaging of the culprit lesion was performed in 70 pts who were divided into 2 groups: VH-TCFA (31 pts) and non-VH-TCFA (39 pts). Plaque rupture was present in 48% (15/31) VH-TCFA vs 30% (12/39) non-VH-TCFA (p=0.15). VH-TCFAs were located in 17 LAD, 3 LCX, and 11 RCA; 70% (22/31) were located in proximal 30mm of each coronary artery. While vessel size, lesion length, plaque burden, and minimal lumen area (MLA) were similar, VH-TCFA showed more positive remodeling (RI=1.11¬±0.23 vs 1.00¬±0.18 in non-VH-TCFA, p=0.055). Maximal NC (37.57¬±11.27% vs 24.16¬±9.43%, p<0.0001) and maximal dense calcium (28.89¬±15.47% vs 20.47¬±14.72%, p=0.035) were larger in VH-TCFA than non-VH-TCFA. Sensitivity/specificity curve analysis (Figure) showed that a MLA of 3.5mm2, a distal reference lumen area of 7.5mm2, and a maximum necrotic core area of 35% best predicted plaque rupture. However, ROC analysis showed that the distal reference lumen area was more predictable of plaque rupture than the maximal NC area. Conclusion. VH-TCFAS were more prone to rupture in larger vessels with a greater % necrotic core area. However non-VH-TCFAs were also common in culprit lesions in STEMI pts.
|
|
|
Warning: getimagesize(/home/virtual/circulationadmin/renewal/econgress/conference/abstract/img_files/RP.jpg) [function.getimagesize]: failed to open stream: No such file or directory in /home/virtual/circulationadmin/new/econgress/conference/manage/schedule/view_abstract.php on line 164
|
|





