| єя«•«ьљƒ : ±Єњђ
|
ЅҐЉцєш»£ - 500754 176 |
| The association between plasma osteoprotegerin level and carotid plaque calcification in coronary artery disease |
| к∞АнЖ®л¶≠ мЭШк≥Љ лМАнХЩ мИЬнЩШкЄ∞ лВік≥Љ |
| мµЬмЪ©мЫР, мЬ§нШЄм§С, мµЬмЬ§мДЭ,мЭілПЩнШД,л∞Хм≤†мИШ,мШ§мЪ©мДЭ,м†ХмЪ±мД±,кєАмЮђнШХ,мµЬкЈЬл≥і,нЩНмИЬм°∞ |
Background :Osteoprotegerin (OPG) is a member of the tumor necrosis factor superfamily involved in the regulation of bone metabolism and vascular calcification. High serum values of OPG are associated with cardiovascular disease in humans. The purpose was to investigate the association between plasma OPG levels and carotid plaque calcification. Subjects and Method:
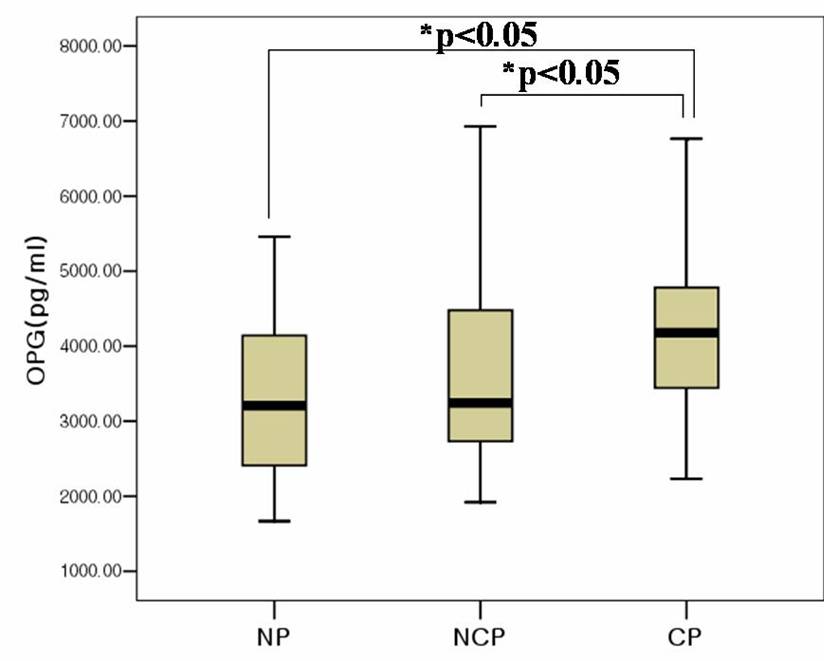
The plasma OPG levels were compared in 147 patients(mean age: 68±7yrs, M:F=82:65)with coronary artery disease. We classified the subjects as the group with calcified carotid plaque(CP)(n=39(27%)), noncalcified carotid plaque(NCP) (n=54(37%)), and the group without plaque(NP)(n=54(37%)). We intentionally selected the patients to be similarly distributed in terms of atherosclerotic risk burden in all groups. Result:1. There is no significant difference between the groups in the distribution of age, diabetes mellitus, hypertension, dyslipidemia. 2. The plasma OPG level was significantly increased in CP group compared with NCP group(median(interquarile range), 4182(1415) vs 3239(1807)pg/ml, p<0.05) or NP group(4182(1415) vs 3204(1754)pg/ml, p<0.05). 3. The difference between NCP and NP group was not significant. Conclusion :
The present study demonstrates increase plasma OPG levels in patients with calcified carotid plaque and it suggests that OPG might have an important role in arterial calcification.
|
|
|
Warning: getimagesize(/home/virtual/circulationadmin/htdocs/econgress/conference/abstract/img_files/5555.jpg) [function.getimagesize]: failed to open stream: No such file or directory in /home/virtual/circulationadmin/new/econgress/conference/manage/schedule/view_abstract.php on line 164
|
|



