| єя«•«ьљƒ : ∆чљЇ≈Ќ
|
ЅҐЉцєш»£ - 500426 151 |
| N-Terminal Pro–B-Type Natriuretic Peptide is associated with an Adverse Short-term Outcomes in Patients with Acute Myocardial Infarction; a KAMIR substudy |
| к±імЦСлМАнХЩкµРл≥СмЫР мЛђмЮ•лВік≥Љ¬є , KAMI мЧ∞кµђмЮР¬≤ , Steering Committee member¬≥ |
| кґМнГЭкЈЉ¬є, л∞∞мЮ•нШЄ¬є ,кєАмШБм°∞¬≤ ,м°∞л™Ем∞ђ¬≤ , кєАмҐЕмІД¬≤ , мХИмШБкЈЉ¬≤ ,м†ХмЪ±мД±¬≤ ,м†Хл™ЕнШЄ¬≤ ,мКєкЄ∞л∞∞¬≥ ,мЮ•мЦСмИШ¬≥,л∞ХмКєм†Х¬≥ |
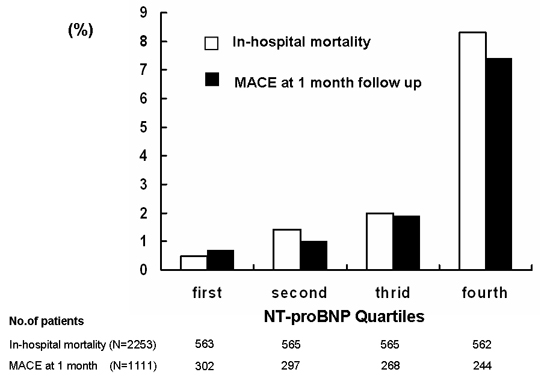
Background; Increased level of N-Terminal Pro–B-Type Natriuretic Peptide (NT-proBNP) is known to be associated with adverse outcome in patients with acute coronary syndrome. We evaluated early outcomes of patients with acute myocardial infarction (AMI) according to the level of NT-proBNP as a substudy of KAMIR (Korean Acute Myocardial Infarction Registry). Method and Results; Study population consisted of 2253 patients (mean 64 years old, male 68.2%) who had baseline NT-proBNP level by electrochemiluminiscence immunoassay (ECLIA, NT-proBNP kit, Roche Diagnostics, Mannheim, Germany). The highest quartile group demonstrated a significantly lower left ventricular ejection fraction than the other quartiles (quartile 1=55.3¬±11.3%, quartile 2=54.8¬±11.01%, quartile 3=51.4¬±11.2%, and quartile 4=44.3¬±12.6%, P<.001). In-hospital mortality rate was increased according to the higher quartile group (quartile 1= 0.5% ; quartile 2=1.4% , quartile 3=2.0%; quartile 4=8.3% , P<.001). Increased quartiles are also associated with the increased major cardiovascular adverse event (cardiac and noncardiac death, MI, revascularization, and coronary artery bypass surgery) rates at 1 month follow up (quartile 1 =0.7% ; quartile 2=1.0% ; quartile 3=1.9% ; quartile 4= 7.4% , P<.001). Conclusions: Increased baseline level of NT-proBNP is associated with adverse in-hospital mortality and MACE rate at 1 month follow-up. This study suggests that baseline NT-proBNP level can be used as a short-term prognostic factor in patients with AMI.
|
|
|
Warning: getimagesize(/home/virtual/circulationadmin/htdocs/econgress/conference/abstract/img_files/proBNP1.jpg) [function.getimagesize]: failed to open stream: No such file or directory in /home/virtual/circulationadmin/new/econgress/conference/manage/schedule/view_abstract.php on line 164
|
|



