| №ЯЗҘЗьҪД : ЖчҪәЕН
|
Бўјц№шИЈ - 490820 185 |
| The Change of Plasma N-Terminal Pro-Brain Natriuretic Peptide Levels after Coronary Stent Implantation in Patients with Normal Left Ventricualr Systolic Function |
| Division of Cardiology, Internal Medicine, Yeungnam University Hospital, Daegu, Korea |
| Hyung-Jun Kim, Jong-Seon Park, Dong-Gu Shin, Gu-Ru Hong, Jun-Ho Bae, Young-Jo Kim, Bong Sup Shim |
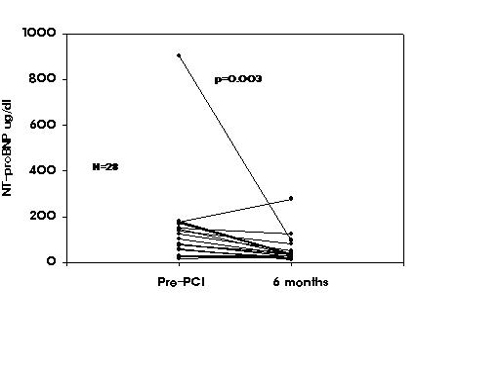
Background: Brain natriuretic peptide and N-terminal-proBNP (NT-proBNP) are established useful biomarkers for the assessment of left ventricular dysfunction. But NT-proBNP has an advantage in the detection of asymptomatic or mild cardiac dysfunction. We sought to determine whether percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) decrease the cardiac secretion of this prognostic marker in angina patients with normal left ventricular systolic function (LVSF).
Method : Successful coronary stent implantation was performed in 28 angina patients without previous myocardial infarction (male 15, age 61Вұ7 years old). Serial NT-proBNP were measured from peripheral blood, before and 6 months after the procedure. To see the effect of coronary stenting, NT-proBNP was measured after PCI in 19 patients. Cardiac function was evaluated by echocardiography before PCI. Results : Pre-PCI echocardiography showed normal LV wall motion in 26 patients with ejection fraction 63Вұ7 %. There was no correlation between left ventricular ejection fraction and NT-proBNP level before PCI (r=.270, p=.249). After PCI, NT-proBNP level was elevated in 74% ,and decreased in 26% of the patients. At 6 months follow up, pre-PCI NT-proBNP levels were significantly decreased in 24 of 28 patients. Restenosis was found in 2 patients, but didnвҖҷt show significant increase of NT-proBNP. Conclusion : Elevate NT-proBNP levels maybe reveal the hidden cardiomyte dysfunction undetectable by echocardiograpy. And coronary intervention could decrease cardiac secretion of the compensatory cardiac cytokine.
|
|
|
Warning: getimagesize(/home/virtual/circulationadmin/htdocs/econgress/conference/abstract/img_files/BNP.jpg) [function.getimagesize]: failed to open stream: No such file or directory in /home/virtual/circulationadmin/new/econgress/conference/manage/schedule/view_abstract.php on line 164
|
|

