| №ЯЗҘЗьҪД : ЖчҪәЕН
|
Бўјц№шИЈ - 480512 270 |
| Increased Arterial Stiffness in Patients with Cardiac Syndrome X |
| Division of Cardiology, Internal Medicine, Dongsan Medical Center, Keimyung University |
| Young-Soo Lee, Kee-Sik Kim, Chang-Wook Park, Min-Jung Kim, Yun-Kyeong Cho, Kuo-Soo Kim, Chang-Wook Nam, Sang-Hoon Lee, Seong-Wook Han, Seung-Ho Hur, Yoon-Nyun Kim, Kwon-Bae Kim |
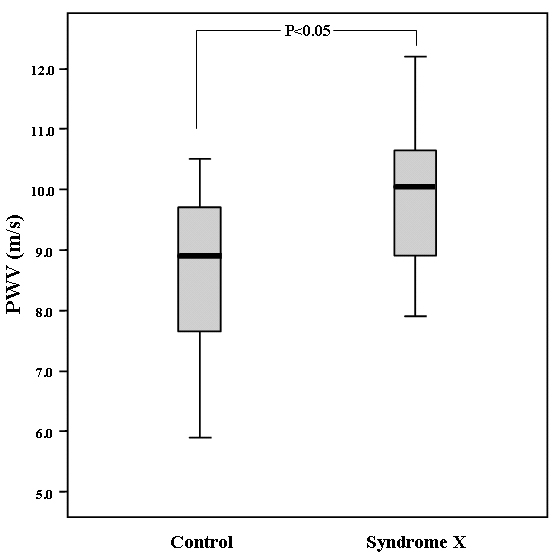
Purpose:Up to 10% of coronary angiogram performed for assessment of chest pain show normal coronary anatomy. Arterial dysfunction has been reported in cardiac syndrome X(CSX), which is characterized by the presence of typical chest pain, positive stress test and normal coronary anatomy. Pulse wave velocity(PWV) has been known as indicator of arterial dysfunction. The aim of this study was to evaluate atherosclerotic risk factor and arterial stiffness by measuring PWV in CSX. Methods:We enrolled 43 patients with typical chest pain and normal coronary anatomy. The CSX group was consisted of 24 patients(male 4, mean 56yrs) with positive stress test. The control was 19 patients(male 11, mean 54yrs), who diagnosed to gastro-esophageal disorder. Arterial stiffness was assessed by measuring carotid-radial PWV. Also, the cardiovascular risk factors including body mass index, lipid profile, left ventricular mass, pulse pressure(PP), plasma homocysteine, and C-reactive protein were measured. Results:PWV was significantly higher in CSX group than in controls(9.90Вұ1.15 vs 8.62Вұ1.32m/s, respectively, p<0.05). Systolic blood pressure and PP in patients with CSX were significantly higher than those in controls, respectively(p<0.05). There was no difference of other atherosclerotic risk factors. The cutoff value for PWV was 8.5m/s(sensitivity:88%, specificity:42%). Conclusions:Increased arterial stiffness and high PP was observed in CSX. PWV assessment may be useful to identify abnormal vascular physiology in these patients.
|
|
|
Warning: getimagesize(/home/virtual/circulationadmin/htdocs/econgress/conference/abstract/img_files/FiginMVA.jpg) [function.getimagesize]: failed to open stream: No such file or directory in /home/virtual/circulationadmin/new/econgress/conference/manage/schedule/view_abstract.php on line 164
|
|




