| №ЯЗҘЗьҪД : ұёҝ¬
|
Бўјц№шИЈ - 480451 179 |
| May Post-Systolic Motion during Dobutamine Stress Echocardiography Predict the Residual Ischemia After Successful Percutaneous Coronary Intervention? |
| Division of Cardiology, Internal Medicine, Dongsan Medical Center, Keimyung University |
| Young-Soo Lee, Kee-Sik Kim, Chang-Wook Nam, Sang-Hoon Lee, Seong-Wook Han, Seung-Ho Hur, Yoon-Nyun Kim, Kwon-Bae Kim |
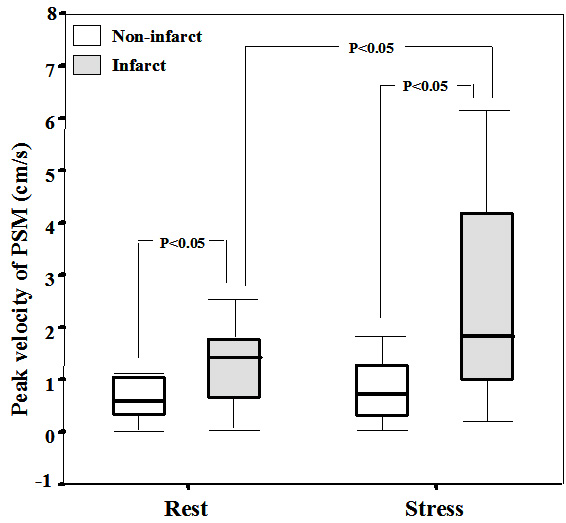
Purpose: Doppler myocardial imaging (DMI) has been suggested as a method of quantifying induced ischemia during dobutamine stress echocardiography (DSE). Post-systolic motion (PSM) detected by DMI is related with peri-infarct ischemia at DSE. The aim of this study is to evaluate the efficacy of PSM to detect residual ischemia after PCI. We compared DMI of the infarct and non-infarct related coronary artery after successful PCI. Methods: DMI was recorded at each stage of a DSE in 15 anterior myocardial infarction patients (15 male, 57.6Вұ12.9 years) and 20 chronic stable angina (10 male, 61.3Вұ8.6 years) at 4 weeks after successful PCI at left anterior descending coronary artery (LAD). Myocardial velocity data were measured in the mid-septal, apical septal, and basal anterior segment of LAD territory. PSM was defined as positive wave, which appeared after the curve of systolic ejection had reached the zero line. Results: The PSM velocity at rest and stress, ratio PSM and S velocity at stress and change of PSM velocity in infarct segment were significantly faster than those in non-infarct segment. Conclusions: The PSM detected by DMI during DSE may predict residual ischemia after successful PCI.
|
|
|
Warning: getimagesize(/home/virtual/circulationadmin/htdocs/econgress/conference/abstract/img_files/DSE.jpg) [function.getimagesize]: failed to open stream: No such file or directory in /home/virtual/circulationadmin/new/econgress/conference/manage/schedule/view_abstract.php on line 164
|
|




